How to Secure Your Cloud Data with Rules-based Engine

Posted By
Mukti Chowkwale
How to Secure Your Cloud Data with Rules-based Engine
Cloud computing offers scalable on-demand services to consumers with greater flexibility and lesser infrastructure investment. Since cloud services are delivered using classical network protocols and formats over the Internet, implicit vulnerabilities existing in these protocols and threats introduced by newer architectures raise many security and privacy concerns.
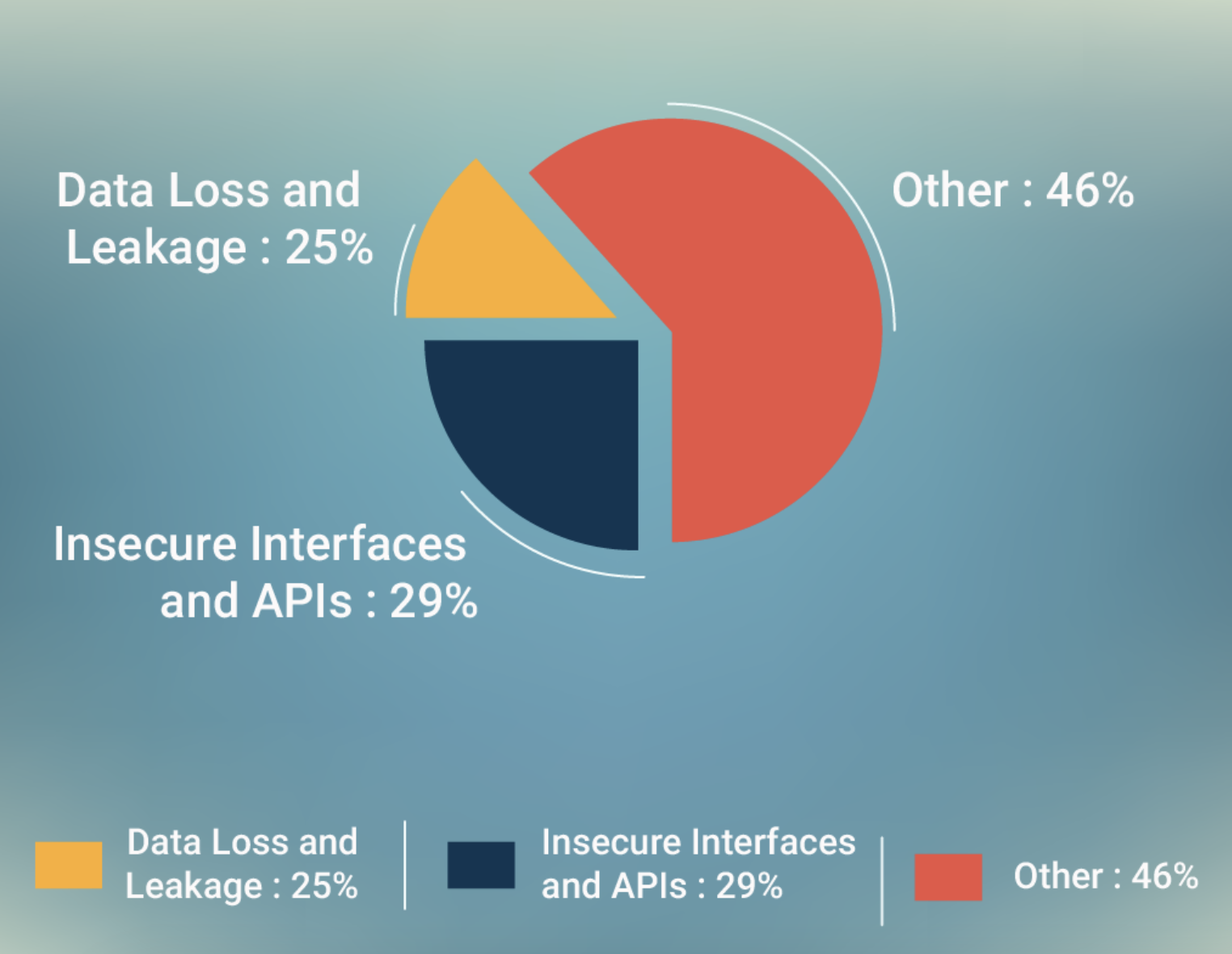
There are many questions that arise as to whether a cloud is secure enough. Numerous threats exist, like insecure interfaces and APIs, malicious insider attacks, data loss and leakage, account or service hijacking, unknown risk profiles, etc. If a cloud service provider relies on a weak set of APIs, various security issues related to confidentiality, integrity, availability, and accountability will be raised. A malicious insider can easily obtain passwords, cryptographic keys, and files, causing fraud, damage, or theft of information and misuse of IT resources. Data loss can occur due to operational failures, unreliable data storage, and inconsistent use of encryption keys.
Approaches to Detecting Attacks
Regarding detecting attacks, there are generally two different approaches: behavior-based and knowledge-based. The behavior-based method dictates how to compare recent user actions to the usual behavior, while the knowledge-based method detects known trails left by attacks or certain sequences of actions from a user who might represent an attack. Behavior-based methods use machine learning, data mining, etc to learn from previous actions and compare them with current ones. Since these methods use patterns learned from previous actions, they can predict new attacks, i.e., attacks that are new. However, many of these methods are not as efficient as knowledge-based methods, which detect attacks by comparing the current action to signatures of previous actions.
Our approach uses a knowledge-based method, with a rules engine designed to use a set of signatures called rules to define what actually constitutes an attack. Rules are signature sets describing significant characteristics of events or specific attack signatures. Rules engines provide an extensive language enabling you to write new rules and extend them to meet your requirements.
System Design
We used the Apache Spark platform to implement the rules engine. It allows data processing at scale and querying that data at scale using SQL-like syntax. This makes Apache Spark a viable option, as it allows the creation of simple rules that can run within stream windows of time and make decisions with the ease of SQL queries. As a result, it can be used as a data aggregation/event processing and analytics platform. Using Apache Spark Streaming, live data from the cloud was analyzed. This includes all traffic related to virtual hosts in the cloud.
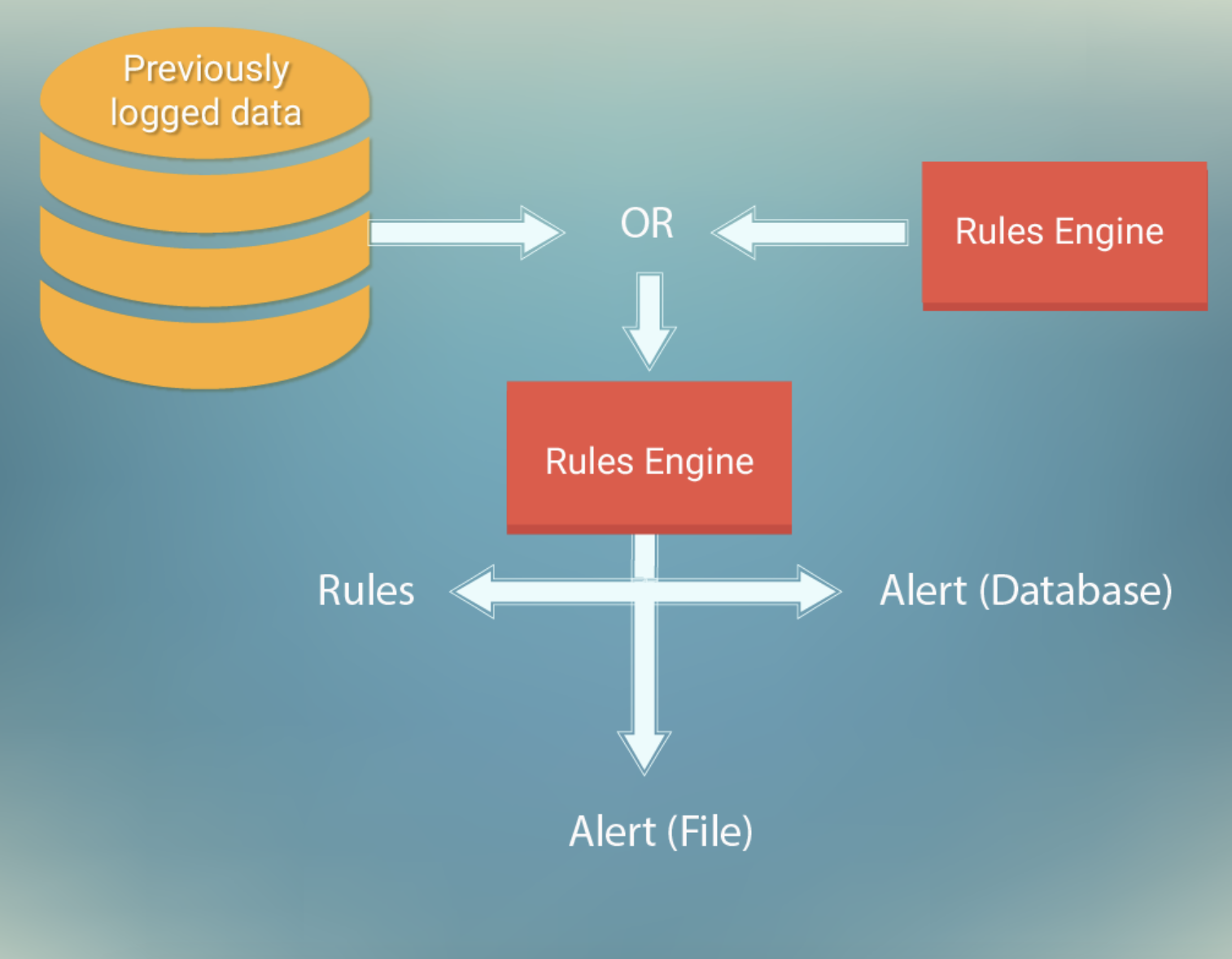
Rules contain information about the type of action to perform when the rule is matched, source and destination IP addresses and ports, and the type of action to perform on packets to check whether they match the rule. Furthermore, it can also contain byte sequences to check against the packet’s payload. Typically, attack signatures are searched for in the payload of packets, and rules matching the content of such payloads are logged using one of the many available logging facilities, alongside information allowing the identification of the traffic flow transporting attack-related traffic. For example, one of the rules limited the number of POST requests to any host. The previously logged data is stored using MongoDB. This data is retrieved by Apache Spark using an SQL-like syntax. This data is then passed to the rules engine, where the system decides whether the current data is an attack.
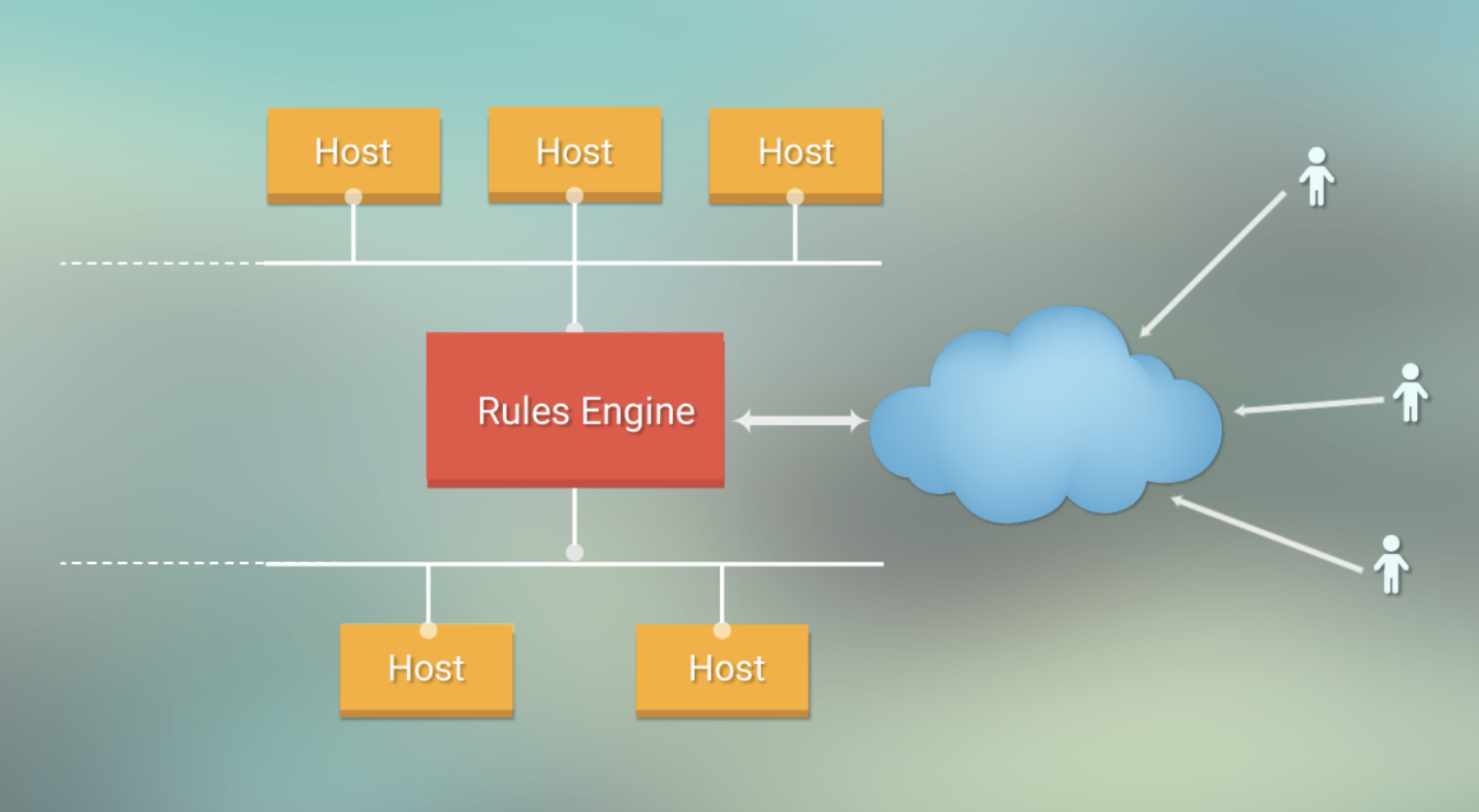
Each host in the cloud is connected to the rules engine, thus allowing all the traffic to be monitored by the system.
Future Scope
Knowledge-based systems are characterized by a high hit rate of known attacks. However, it cannot detect new attacks. This system can be improved by pairing this with a behavior-based system, thus allowing the detection of new attacks while efficiently detecting known attacks. Also, as there is one rules engine for multiple hosts, the engine can get overloaded, thus becoming a bottleneck. This can be avoided by using multiple rules engines for multiple hosts.
Cloud computing is a “network of networks” over the internet; therefore, the chances of malicious attacks are more with the erudition of the attacker. Our system allows the client to customize the security rules, thus allowing them to filter traffic according to their growing requirements and new attacking patterns. Its advantages include a high detection rate, low false positives, and negatives rate, and the ability to analyze live data traffic. Eradication of malicious attacks over the cloud will deal with the majority of the security problems in the cloud, thus allowing safe and easy usage.